Stat Cafe - Samuel Gailliot

Data Sketching and Stacking: A Confluence of Two Strategies for Predictive Inference in Gaussian Process Regressions with High-Dimensional Features
- Time: Monday 2/19/2024 from 11:40 AM to 12:30 PM
- Location: BLOC 448
- Pizza and drinks provided
Description
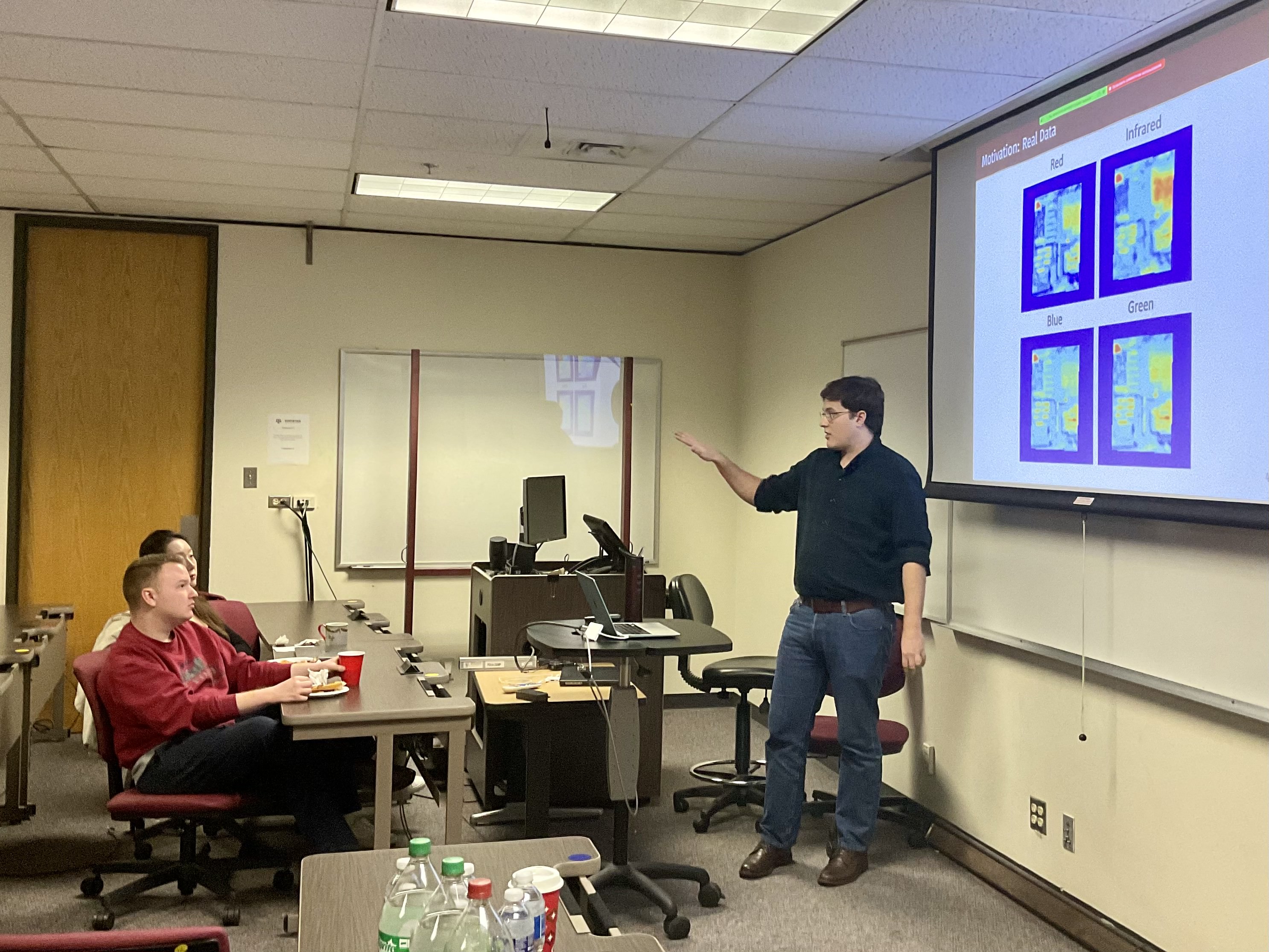
This article focuses on drawing computationally-efficient predictive inference from Gaussian process (GP) regressions with a large number of features when the response is conditionally independent of the features given the projection to a noisy low dimensional manifold. Bayesian estimation of the regression relationship using Markov Chain Monte Carlo and subsequent predictive inference is computationally prohibitive and may lead to inferential inaccuracies since accurate variable selection is essentially impossible in such high-dimensional GP regressions. As an alternative, this article proposes a strategy to sketch the high-dimensional feature vector with a carefully constructed sketching matrix, before fitting a GP with the scalar outcome and the sketched feature vector to draw predictive inference. The analysis is performed in parallel with many different sketching matrices and smoothing parameters in different processors, and the predictive inferences are combined using Bayesian predictive stacking. Since posterior predictive distribution in each processor is analytically tractable, the algorithm allows bypassing the robustness issues due to convergence and mixing of MCMC chains, leading to fast implementation with very large number of features. Simulation studies show superior performance of the proposed approach with a wide variety of competitors. The approach outperforms competitors in drawing point prediction with predictive uncertainties of outdoor air pollution from satellite images.
Presentation
Recording
Gallery